Gitlab → Gitfarm Code Replication
Gitlab → Gitfarm Code Replication¶
Dragonfly source code is hosted in a AWS owned instance of Gitlab which is not approved as a tool to mange source code within Amazon yet. We have several repositories hosted on AWS Gitlab besides Dragonfly. In order to be InfoSec compliant we need a way to host the source code within Gitfarm so that Infosec scanners make sure there’s no security risk while we keep using AWS Gitlab to utilize the features available on Gitlab that help with our development process. This doc explores a way to host the code on Gitfarm and make sure all our changes make it to Gitfarm from Gitlab.
Proposed Solution¶
This solution is based on the strategy explored as part of artifact replication setup required to make Dragonfly work with native apps with exported bundles.
We’ll create a CodeCommit repo to host the source code between Gitlab and Gitfarm, code replication is supported from CodeCommit to Gitfarm but not from Gitlab to Gitfarm. We’ll be using the CI process from Gitlab to kick off a code replication step from Gitlab to CodeCommit. Once our source code makes it to CodeCommit, a reverse Pica-Pica integration with Gitfarm will replicate the changes from CodeCommit to Gitfarm. Every step of this process will be automated so that no manual intervention is required to do these steps every time source code is update in Gitlab.
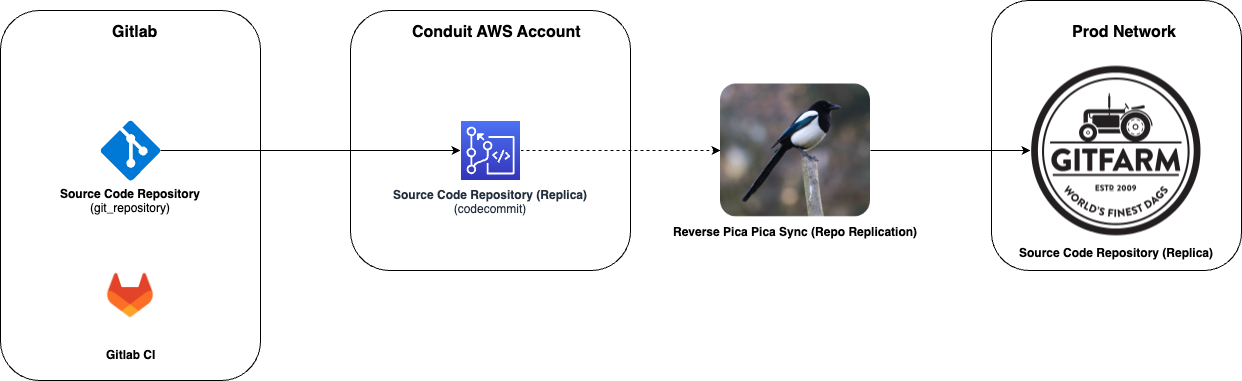
Steps¶
Setup Gitfarm Repository¶
A new code repository needs to be created using BuilderHub create to host the code on Gitfarm. Empty package template should work for this use case.
Setup CodeCommit Repository¶
A CodeCommit repository also needs to be setup to host the replicated code from Gitlab so that it can be replicated to Gitfarm. We can used CDK to setup the code repository. Remember to host the CodeCommit repo only in us-west-2.
Setup IAM Roles¶
We’re using a reverse pica-picasync to replicate code from CodeCommit to Gitfarm. We need to setup roles required for pica-pica to work correctly.
We also need to create a role to allow Gitlab CI runner to publish to CodeCommit.
Setup Replication Between Gitlab & CodeCommit¶
Gitlab CI process can be used to trigger a step that replicates the git branches on Gitlab using the role setup in the previous step. The CI step can be modified according to the project needs for replication. If you only need to push only one or two branches, script can be modified to only push required branches. Make sure the branch is replicated to CodeCommit by navigating to CodeCommit console on AWS.
Replicate Git Data Manually¶
Git data needs to be the same between source (Gitlab/CodeCommit) and destination to setup pica-pica replication. Once a parity is established pica-pica can keep track of the changes and replicate them. To replicate git data manually before setting up pica-pica replication follow these steps:
Assume admin credentials of the AWS account with ada:
ada credentials update —account={account_id} —provider=conduit —role=IibsAdminAccess-DO-NOT-DELETE —once && export AWS_PROFILE=defaultIf the branch that needs replication already exists on Gitfarm then clone the Gitfarm repo locally and delete the branch.
Clone the Gitlab repo locally.
Add the Gitfarm repo remote to the Gitlab remote locally:
git remote add gitfarm ssh://git.amazon.com:2222/pkg/{package_name}Push the branch to Gitfarm:
git push gitfarm {branch_name}
Once the git data is replicated, all three systems (Gitlab, CodeCommit, Gitfarm) should have the same commits on the branch.
Setup Pica-Pica Replication¶
Once the git data parity has been established between CodeCommit and Gitfarm reverse pica-pica sync can be established using PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI:
Clone the CLI locally:
brazil workspace create —name PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI —root PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI —versionSet PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI/development brazil ws use -p PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI cd PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLI/src/PicaPicaConfigurationServiceCLICreate replica:
brazil-runtime-exec picapica -e prod-sentry create-replica-v2 CodeCommit {codecommit_repo_arn} GitFarm {package_name} {pica-pica-role-arn} —ignore-non-empty-destinationCheck replica status:
brazil-runtime-exec picapica -e prod-sentry get-replica-v2 GitFarm {package_name}
Replica status should be “UpToDate” for the replication to work correctly.
{
"replica": {
"sourceType": "CodeCommit",
"sourceId": "arn:aws:codecommit:us-west-2:{account_id}:{package_name}",
"destinationType": "GitFarm",
"destinationId": "{package_name}",
"awsAccountName": "{account_name}",
"lastReplicatedSourceChangeDateUTC": 1689026139551,
"viewDestinationLink": "https://code.amazon.com/packages/{package_name}",
"status": "UpToDate",
"permittedActions": [
"deleteReplica",
"viewInDestinationSystem"
],
"creationDate": 1686169776750
},
"__type": "com.amazon.aws.picapica.configurationservice#GetReplicaV2Output"
}
References¶
Pica-Pica Replication Code - https://gitlab.aws.dev/amazonmusic/musicdragonfly/dragonfly-cdk/-/blob/main/lib/rev-pica-pica-replication-cdk-stack.js
Gitlab to CodeCommit Push - https://gitlab.aws.dev/amazonmusic/musicdragonfly/dragonflyartifact/-/blob/mainline/.gitlab-ci.yml
Monitoring¶
Pica-Pica publishes a PMET metric for individual repositories. Monitors and Alarms can be created on monitorportal and Carnaval to monitor the replication status.
Pica-Pica Documentation - https://w.amazon.com/bin/view/BuilderTools/Groups/Source/Convergence/Runbook/SetupCustomerMetrics/
PMET Alarm - https://monitorportal.amazon.com/monitors/properties?&id=us-west-2:DragonflyArtifact-PicaPica-PushToGitFarm-Alarm
Carnaval Monitor - https://carnaval.amazon.com/v1/viewObject.do?name=DragonflyArtifact+PicaPica+PushToGitFarm+Alarm&type=monitor
